Rosa Turco, Riccardo Tesser, Vincenzo Russo, Rosa Vitiello, Massimo Fagnano, Martino Di Serio
Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. Volume 122, Issue1, January 2020, 1900100 https://doi.org/10.1002/ejlt.201900100
Abstract
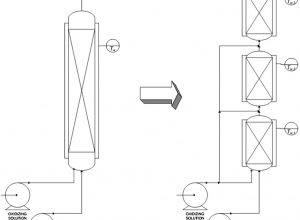
The world production of epoxidized vegetable oil, mainly epoxidized soybean oil, is continuously increasing because this product can have a wide range of applications. Non‐edible vegetable oils, recovered by the plants growing on marginal and polluted lands, represent a possible answer to industry versus food chain debate. Cardoon (Cynara cardunculus L.) seed oil can be considered as an interesting and sustainable alternative to edible soybean oil to make plasticizers. In this work, a comparison between different epoxidation methods of cardoon oil is depicted and argued, focusing on strong points and weaknesses for each of them. It is found that cardoon seed oil can be successfully epoxidized through feasible existing technologies, by peracids and hydrogen peroxide equally. Moreover, it is demonstrated that a “greener” cardoon oil epoxidation process is possible, by using hydrogen peroxide in the presence of commercial γ‐alumina as heterogeneous solid catalyst.
Practical Applications : The paper analyzes the advantages and the problems of different epoxidation methods in order to obtain a final product with high quality and answer the environmental, social, and economic sustainability requirements.